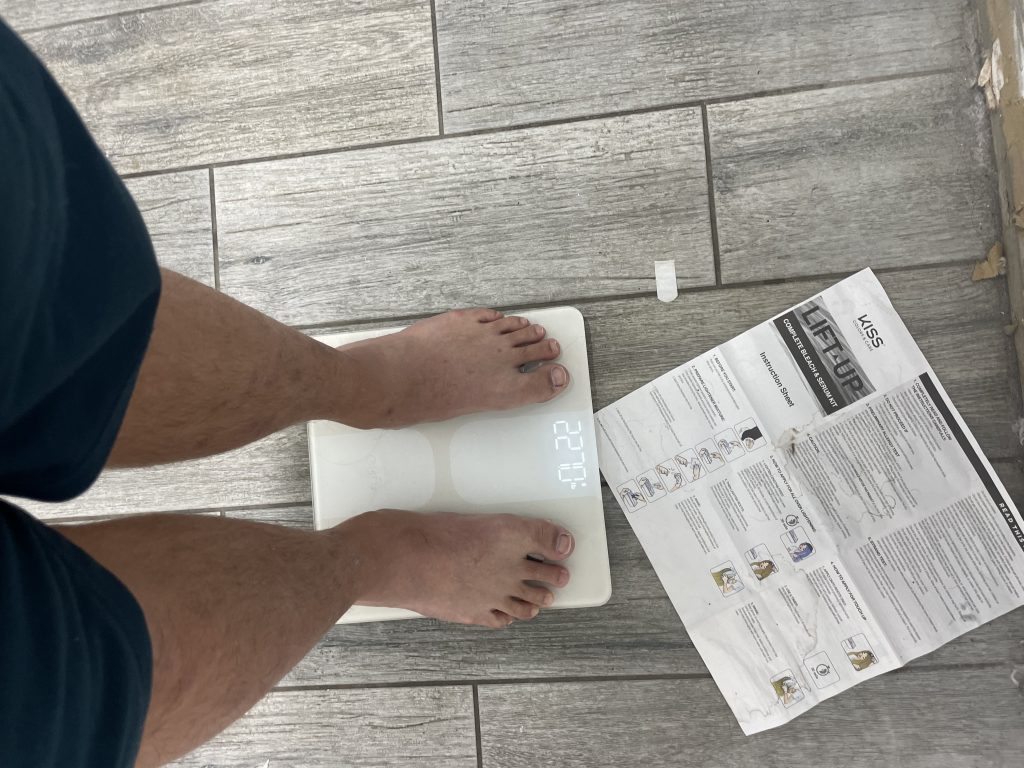
Weigh in 229.2 +2.2lb 4/27/24
Meat-Only Diet Health Benefits
- What is a meat only diet?
- Meat-Only Diet Health Benefits
- Examples
What is a Meat-Only diet?
A meat-only diet, also known as a carnivore diet, all-meat diet, Lion Diet is a dietary approach that primarily consists of consuming only animal products, particularly meat. This means avoiding all plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. Supporters of the carnivore diet argue that humans evolved to eat meat and that eliminating plant foods can lead to various health benefits such as weight loss, improved energy levels, and better digestion.
Health benefits of Meat-Only Diet
- Weight Loss: Some individuals may experience weight loss on a carnivore diet, possibly due to reduced calorie intake or changes in metabolism.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Some proponents suggest that eliminating carbohydrates from the diet can lead to better blood sugar control, potentially benefiting individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance. However, the long-term effects on blood sugar regulation are not well understood.
- Reduced Inflammation: Advocates of the carnivore diet claim that eliminating plant foods, which can contain anti-nutrients and allergens, may reduce inflammation in the body, leading to relief from conditions such as arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. However, scientific evidence supporting this claim is lacking.
- Simplified Digestion: Proponents argue that meat is easier to digest compared to plant foods, leading to improved gastrointestinal health and reduced digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. However, individual responses to different foods can vary widely.
- Mental Clarity and Mood Improvement: Some individuals report experiencing increased mental clarity, improved mood, and reduced brain fog on a carnivore diet, although scientific evidence supporting these claims is lacking.
Examples
- Beef with butter and eggs
- Ground beef with butter and eggs
- Mikhaila Fuller Formally Mikhaila Peterson
Intermittent Fasting: What is it, and how does it work?
- Intermittent Fasting Benefits
- Intermittent Fasting Schedule
Intermittent Fasting Benefits
- Weight Loss.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity
- Cellular Repair and Autophagy
- Heart Health
- Brain Health
- Reduced Inflammation
- Improved Digestive Health
Intermittent Fasting Schedule
There are several intermittent fasting schedules, each with its own unique approach to when and how long you should fast. Here are some popular intermittent fasting schedules:
- 16/8 Method (Leangains Protocol): This involves fasting for 16 hours each day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. For example, you might eat between 12:00 pm and 8:00 pm and fast from 8:00 pm until 12:00 pm the next day.
- 5:2 Diet: With this approach, you eat normally for five days of the week and restrict calorie intake to around 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days. On fasting days, you might consume those calories spread across one or two meals.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: As the name suggests, you alternate between fasting days and non-fasting days. On fasting days, you may either consume no calories or limit calorie intake to around 500 calories. On non-fasting days, you eat normally.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: This method involves fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week. For example, you might fast from dinner one day until dinner the next day.
- Warrior Diet: This approach involves fasting for 20 hours each day and eating one large meal within a 4-hour eating window, typically in the evening.
- OMAD (One Meal A Day): With OMAD, you fast for 23 hours and consume all your daily calories within a 1-hour eating window.
When choosing an intermittent fasting schedule, it’s important to consider your lifestyle, preferences, and any health conditions you may have. It’s also crucial to stay hydrated during fasting periods and to focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods during eating windows to support overall health and well-being.
Sources